Introduction
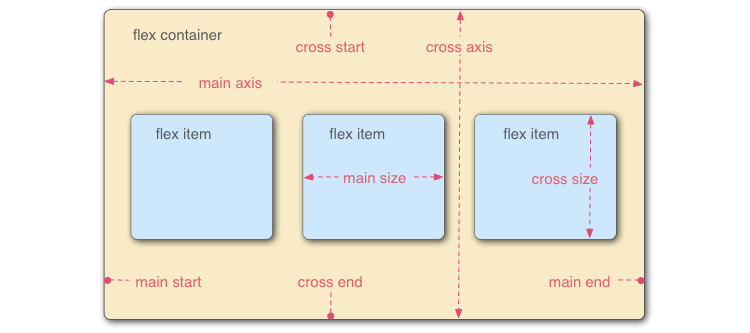
Flexbox (Flexible Box Layout Module) is a modern CSS layout system that provides an efficient way to arrange, align, and distribute space among items in a container. Unlike traditional methods (float, table, inline-block), Flexbox is direction-aware and adapts easily to different screen sizes, making it very useful in responsive web design.